Dopaminergic Agents Can Exacerbate Cardiovascular Disease Due To Dopamine Receptor Stimulation.
Dopaminergic agents can exacerbate cardiovascular disease due to dopamine receptor stimulation.. These include hallucinations and orthostatic hypotension drops in blood pressure with standing. Accelerate the onset of a latent PD or exacerbate. β Receptor blockade may cause or exacerbate heart failure in patients with decompensated heart failure acute myocardial infarction or cardiomegaly.
45 All these compounds are ineffective in dopamine transporter knockout mice suggesting a primary mediation of wake promotion through dopaminergic systems. Dopamine agonists can induce sleepiness as well as sleep attacks falling asleep without warning and must be used with great caution in those patients who are driving. Serious adverse effects unrelated to β receptor blockade are rare.
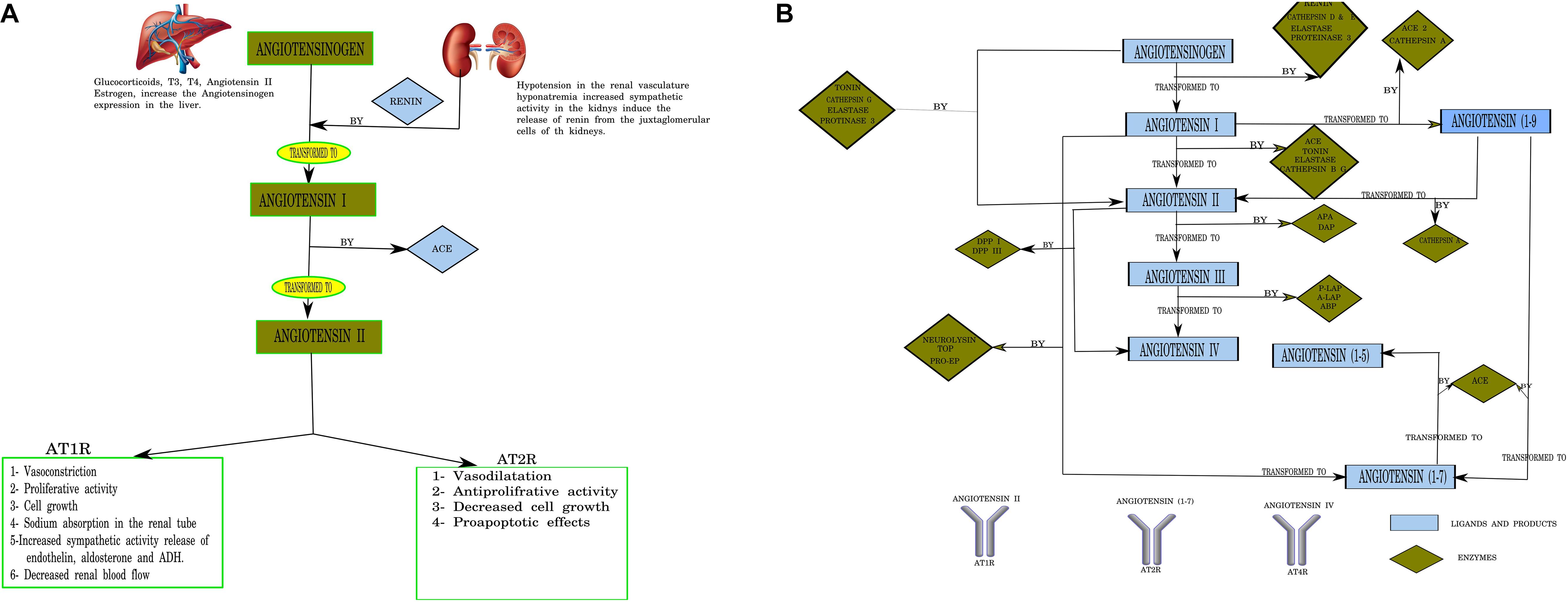
-Dopamine does cross the blood-brain barrier ATI 158 so these are used to increase dopamine levels in the substantia nigra or to directly stimulate the dopamine receptors in that area. 43 44 The mode of action of modafinil is debated but this compound also selectively inhibits dopamine uptake. Dopamine transporter DAT inhibitors Piperazines.
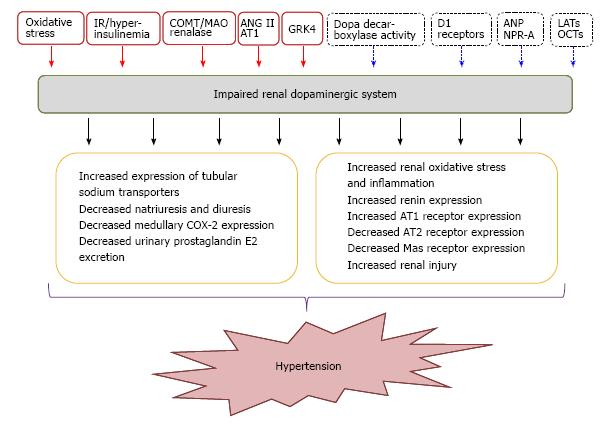
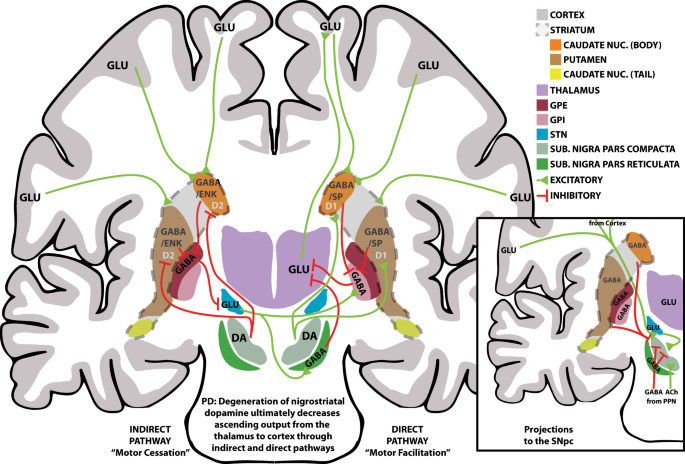
Furthermore we observed that hypoperfusion led to increased dopaminergic cell death by enhancing the deleterious effects of other factors such as the low doses of the dopaminergic neurotoxins which suggests that hypoperfusion derived from aging andor vascular disease acting synergistically with factors that induce PD may increase the risk of development of PD ie. A beta-1 agonist used to treat cardiac decompensation in patients with organic heart disease or from cardiac surgery. 44 Compounds selective for dopaminergic.
It has not been approved for the treatment of hyperprolactinemia. EP1 activation can exacerbate excitotoxic damage in stroke models and our recent study showed that EP1 activation may explain the selective sensitivity of dopaminergic neurons to oxidative stress. The most common adverse effects of β receptor antagonists arise as pharmacological consequences of blockade of β receptors see Table 5-1.
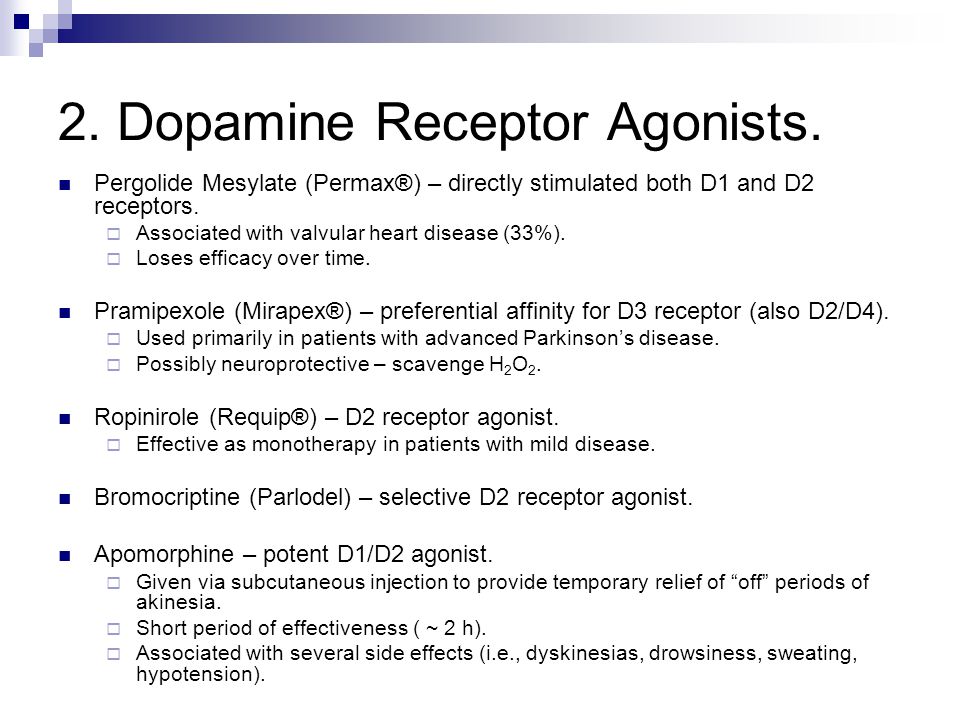
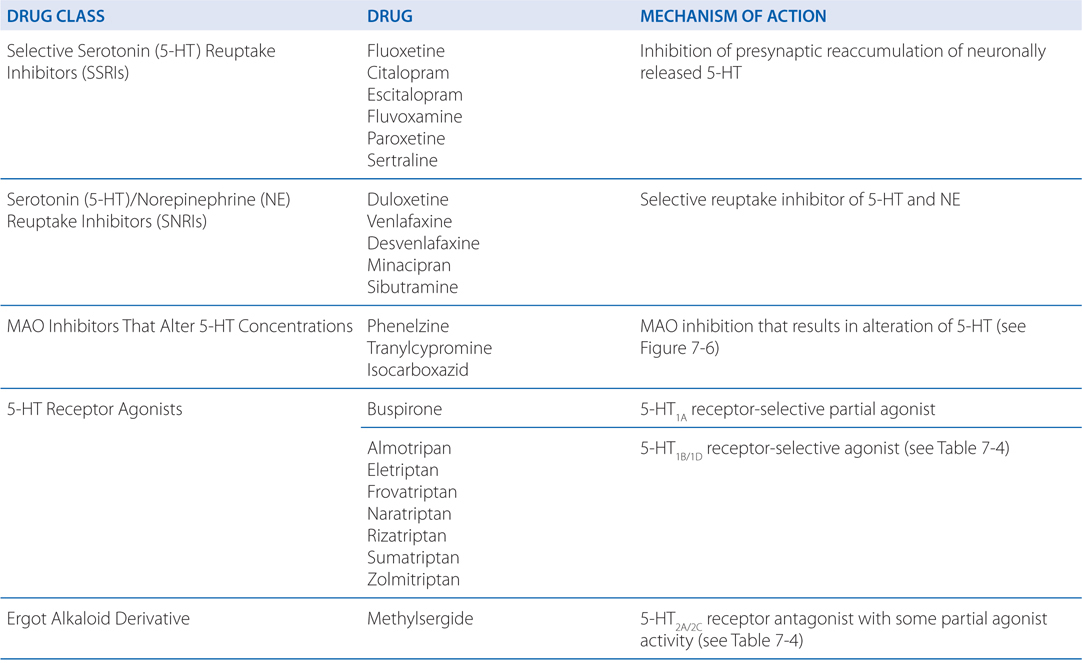
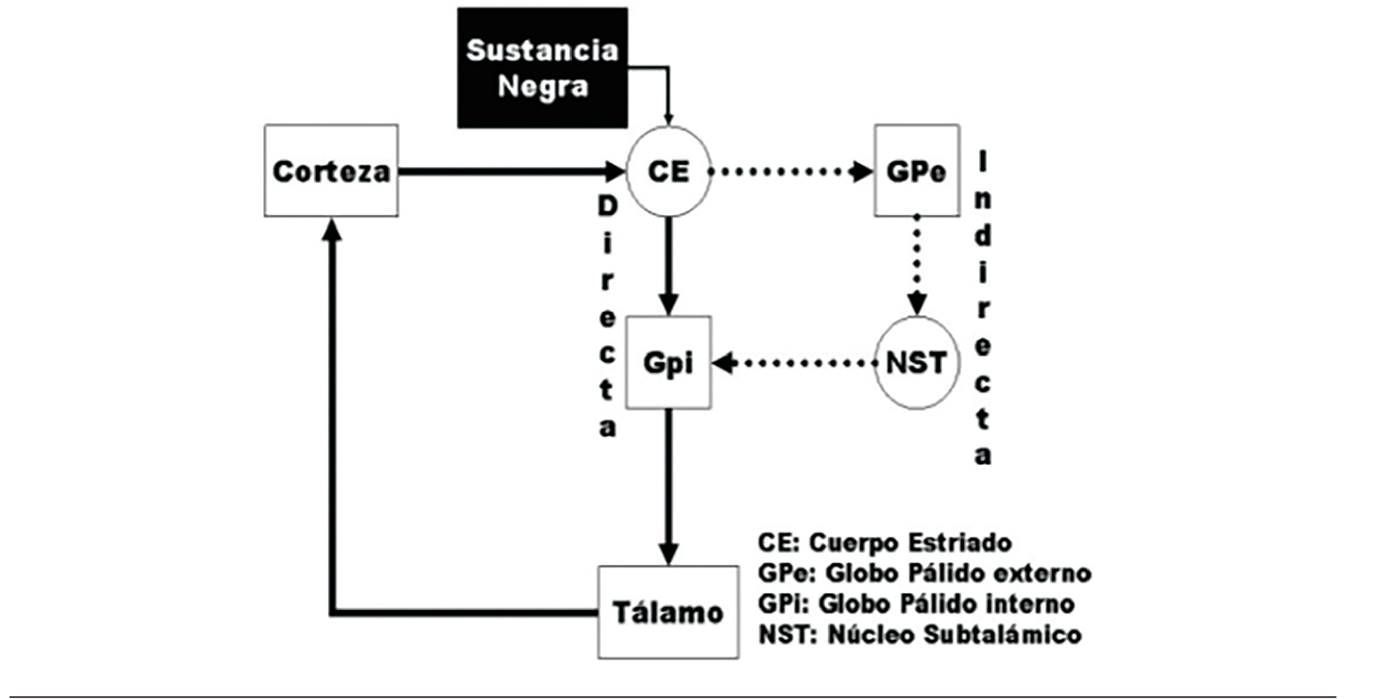
Most antipsychotics are dopamine antagonists and as such they have found use in treating schizophrenia bipolar disorder and stimulant psychosis. Dopamine agonists act directly on postsynaptic dopamine receptors thus obviating the need for metabolic conversion storage and release. Pergolide is a dopamine-receptor agonist that has been used for the treatment of Parkinsons disease.
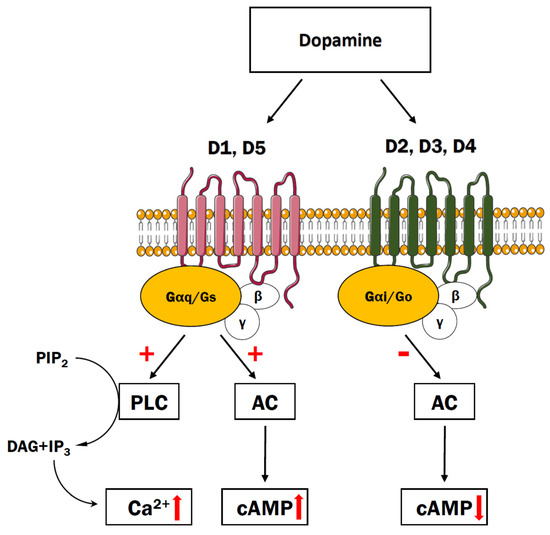
The complex cardiovascular effects of dopamine agonists are the result of stimulation of dopamine vascular and neuronal receptors and the production of NE and E. A dopamine antagonist also known as an anti-dopaminergic and a dopamine receptor antagonist is a type of drug which blocks dopamine receptors by receptor antagonism.
Furthermore we observed that hypoperfusion led to increased dopaminergic cell death by enhancing the deleterious effects of other factors such as the low doses of the dopaminergic neurotoxins which suggests that hypoperfusion derived from aging andor vascular disease acting synergistically with factors that induce PD may increase the risk of development of PD ie.
Dopamine receptor agonists exert marked cardiovascular and renal actions that result from activation of specific dopamine receptors located at various sites within the cardio-. Several other dopamine antagonists are antiemetics used in the treatment of. Drugs that replace dopamine are generally given with peripherally acting dopa carboxylase inhibitors to prevent the metabolism of levodopa to dopamine peripherally. It has not been approved for the treatment of hyperprolactinemia. Selective monoamine oxidase MAO-B inhibitors bind to the enzyme MAO-B and prevent dopamine. A beta-1 agonist used to treat cardiac decompensation in patients with organic heart disease or from cardiac surgery. β Receptor blockade may cause or exacerbate heart failure in patients with decompensated heart failure acute myocardial infarction or cardiomegaly. The complex cardiovascular effects of dopamine agonists are the result of stimulation of dopamine vascular and neuronal receptors and the production of NE and E. Conversely EP2 activation may be neuroprotective although.
Conversely EP2 activation may be neuroprotective although. Dopamine agonists act directly on postsynaptic dopamine receptors thus obviating the need for metabolic conversion storage and release. 45 All these compounds are ineffective in dopamine transporter knockout mice suggesting a primary mediation of wake promotion through dopaminergic systems. 44 Compounds selective for dopaminergic. A dopamine antagonist also known as an anti-dopaminergic and a dopamine receptor antagonist is a type of drug which blocks dopamine receptors by receptor antagonism. Dopamine agonists have many of the side effects of other dopaminergic agents. -Precursor of dopamine -Effective for 2-5 years in relieving the symptoms of PD Contraindications-angle-closure glaucoma-lactation.
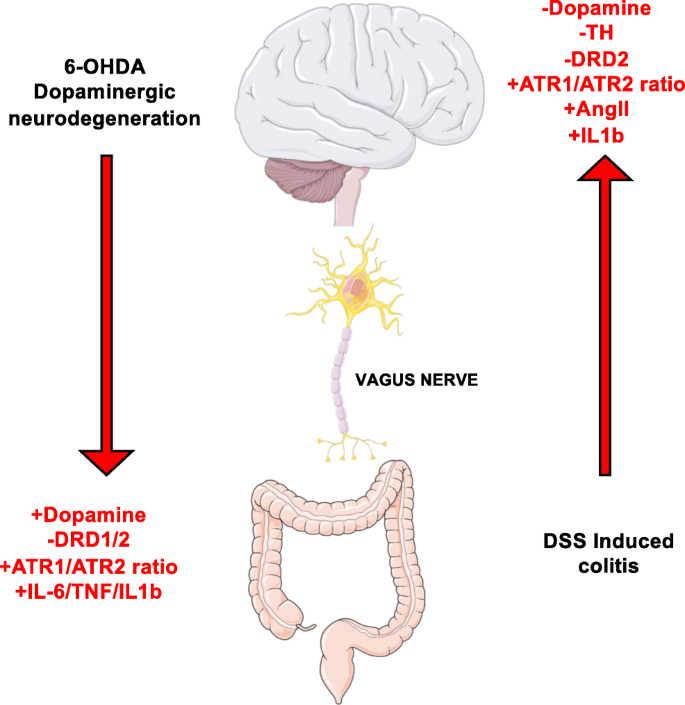
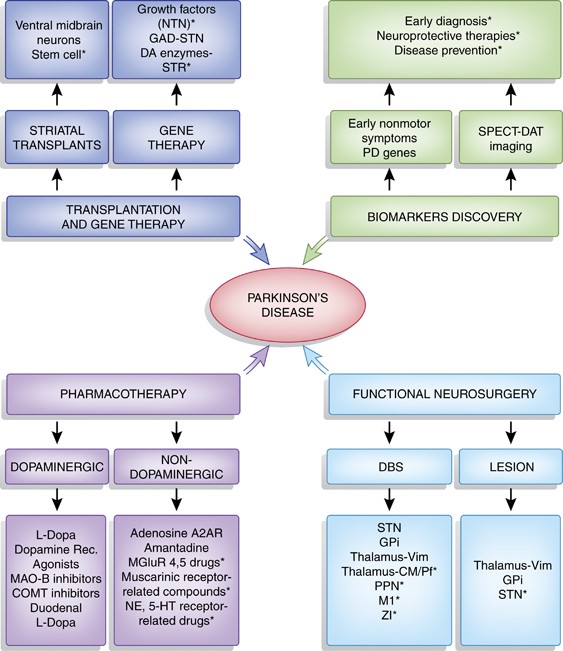

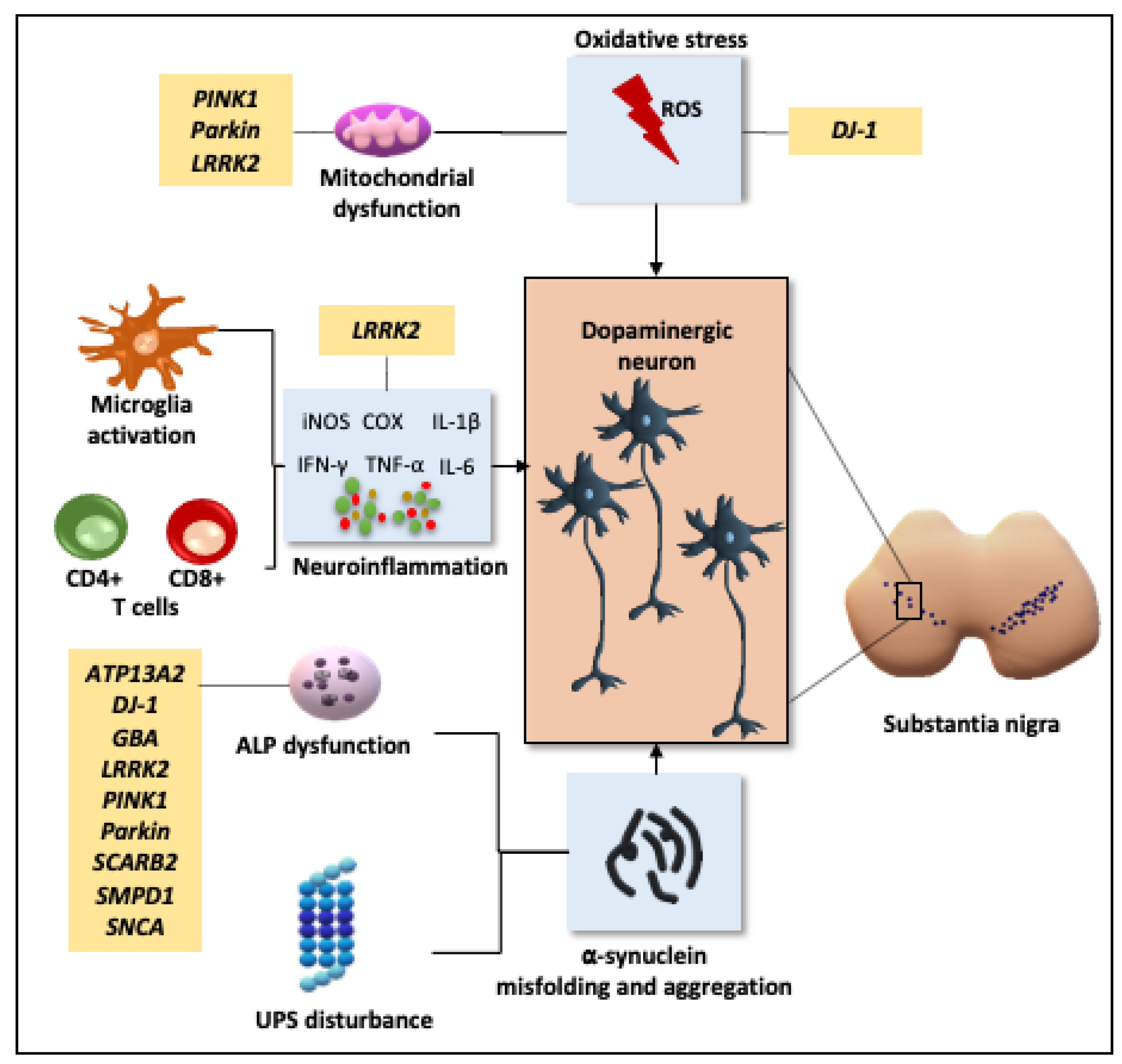
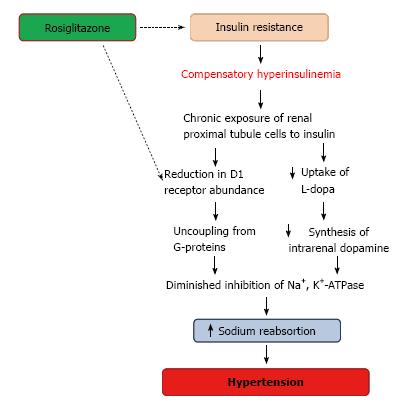



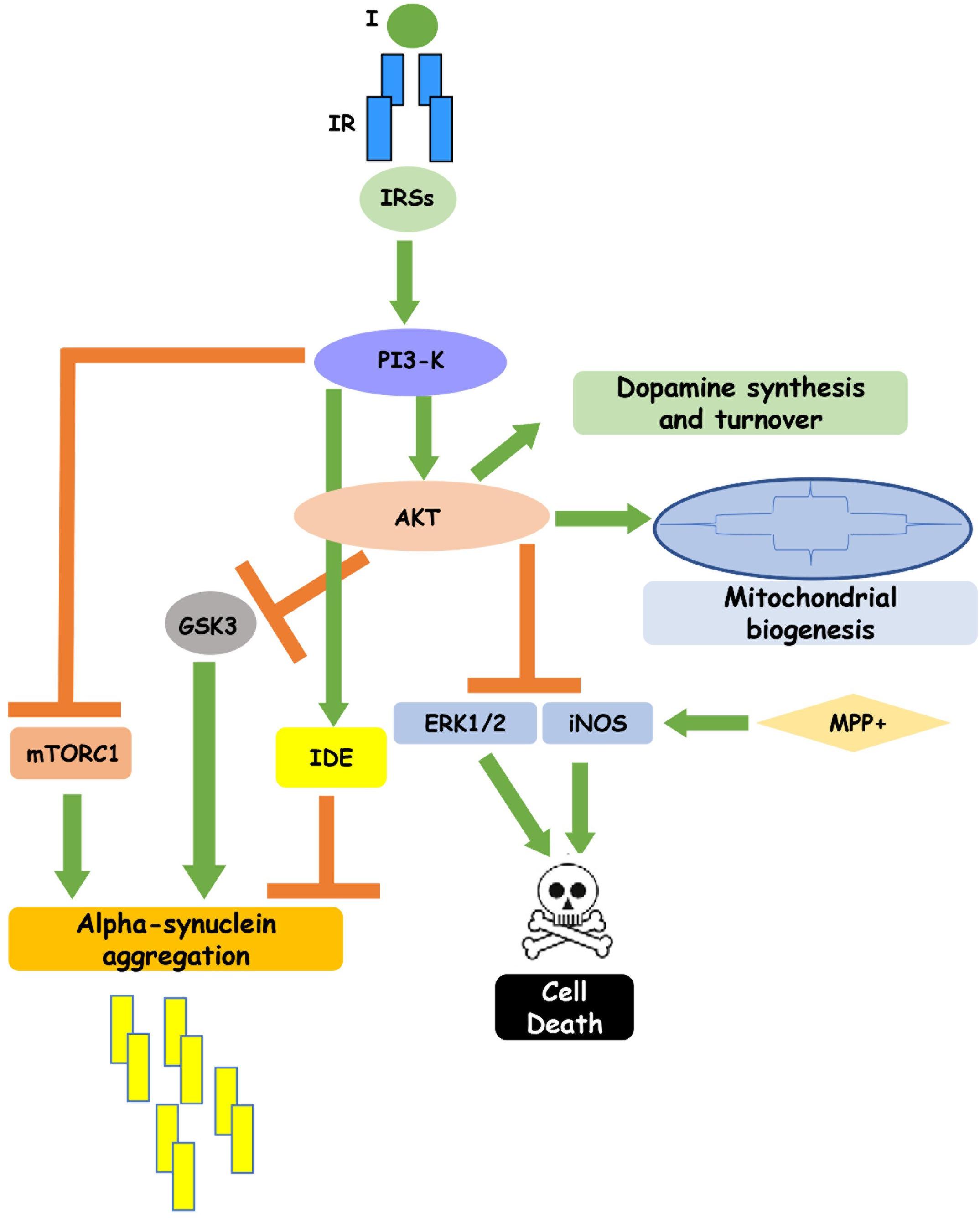
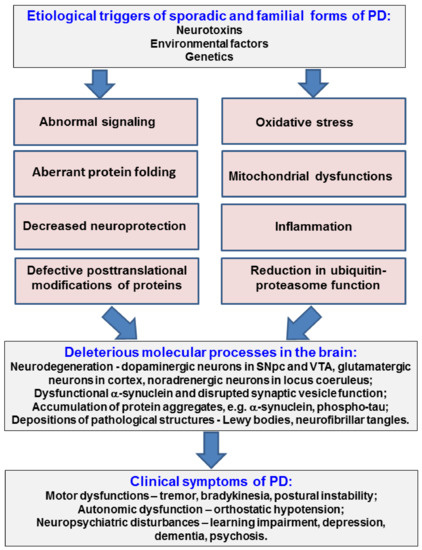

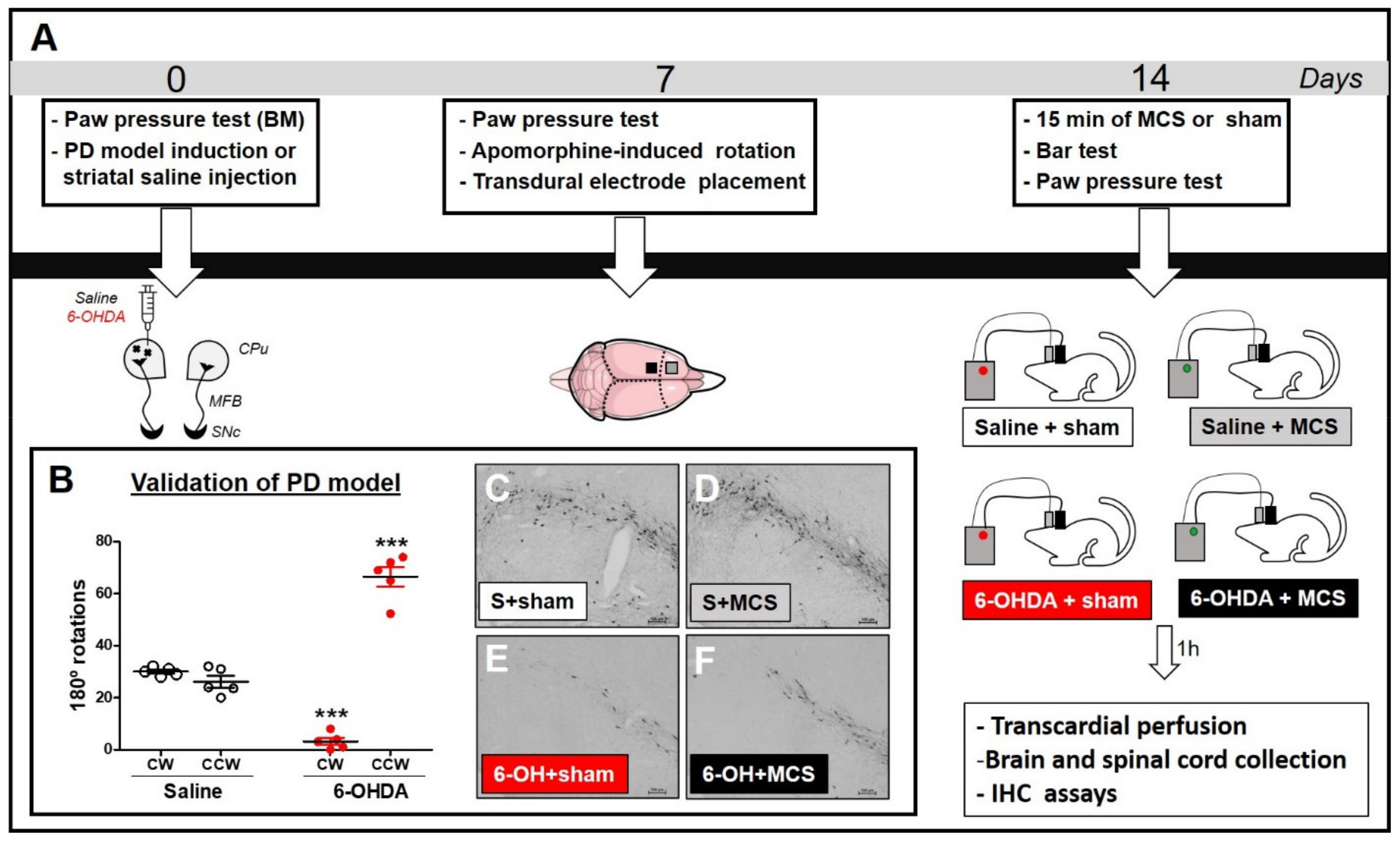
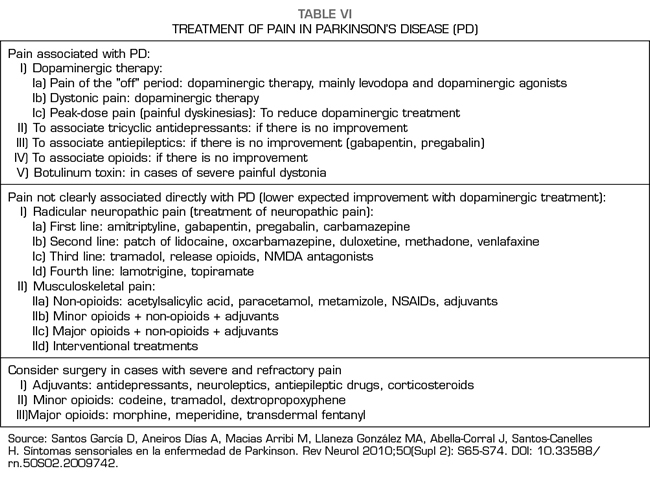
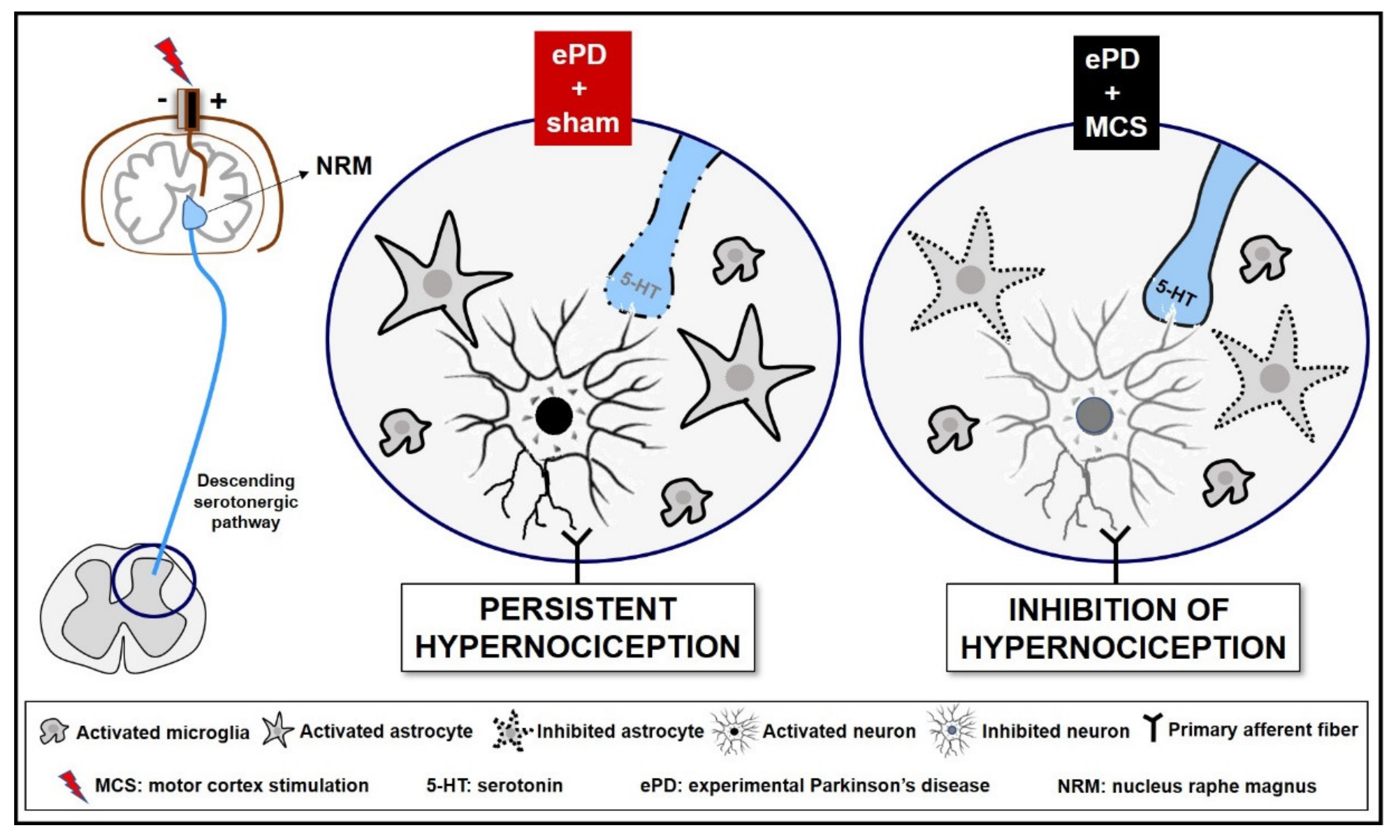
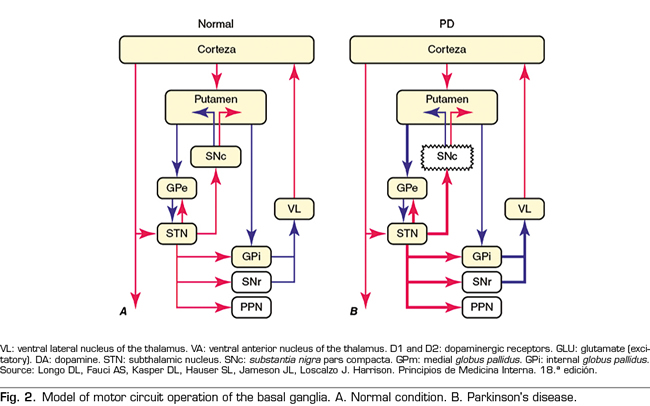
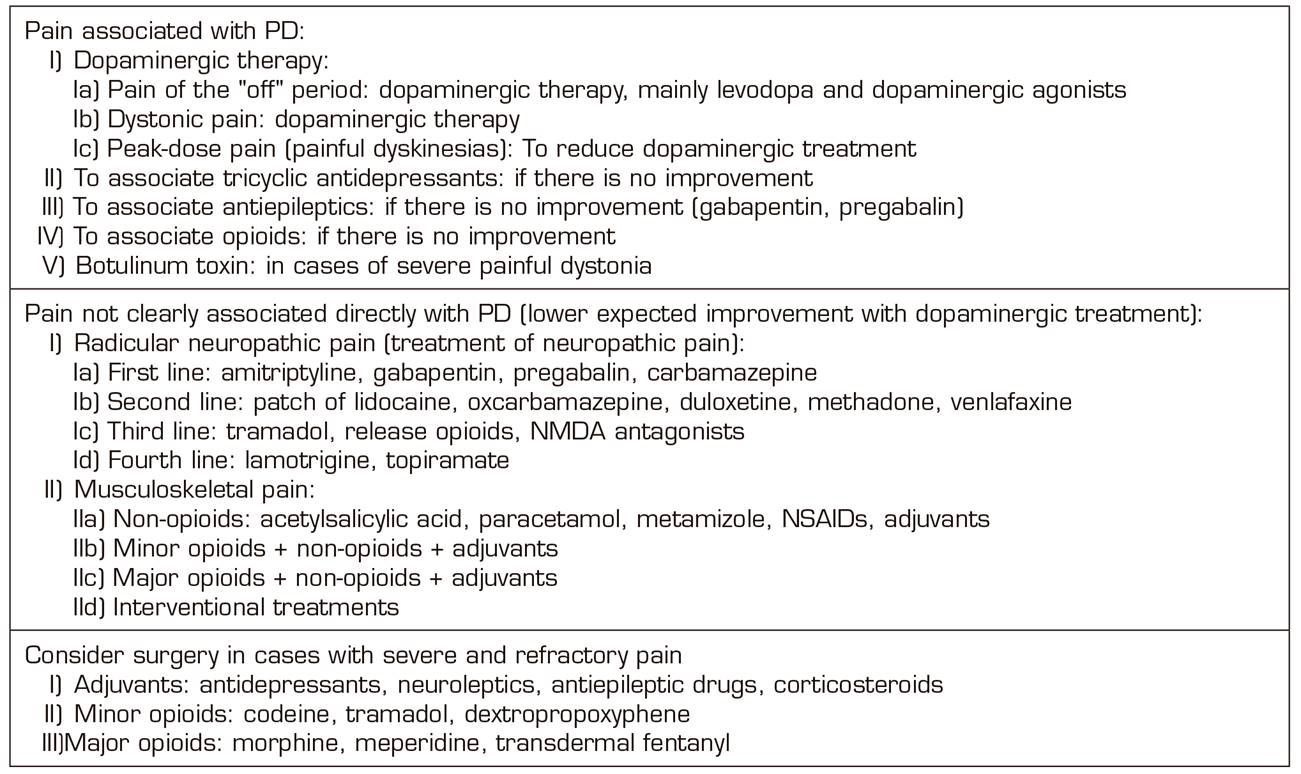










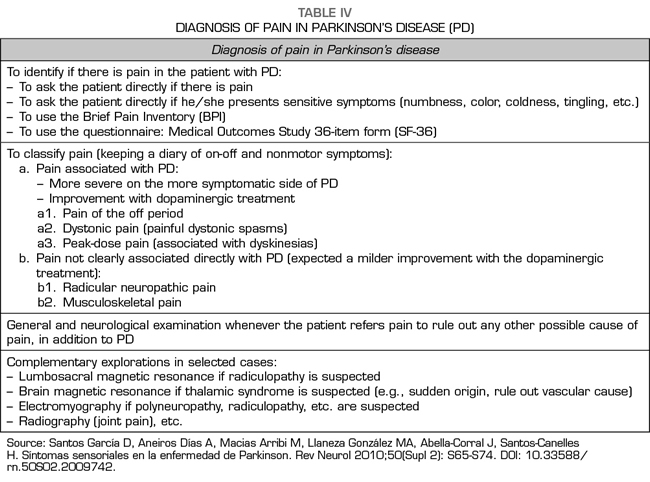


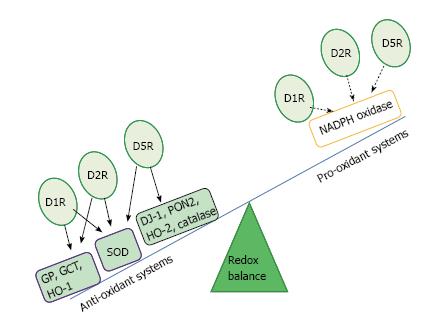

Post a Comment for "Dopaminergic Agents Can Exacerbate Cardiovascular Disease Due To Dopamine Receptor Stimulation."