Bartter Syndrome In Adults
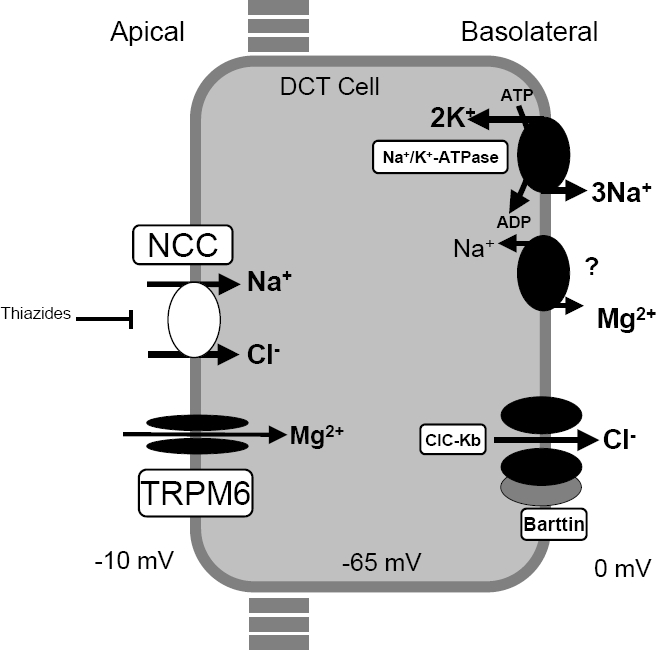
Bartter syndrome in adults. They also affect your kidneys. The disorder is caused by genetic mutations resulting in improper function of the thiazide-sensitive sodium-chloride symporter SLC12A3 also known as NCC NCCT or. To emphasise the rational order starting with simple.
The syndrome is therefore associated with high levels of renin and aldosterone in the blood increased blood pH alkalosis and high levels of potassium calcium. Bartter syndrome and Gitelman syndrome can both cause metabolic alkalosis. Nephritic syndrome is a syndrome comprising signs of nephritis which is kidney disease involving inflammationIt often occurs in the glomerulus where it is called glomerulonephritisGlomerulonephritis is characterized by inflammation and thinning of the glomerular basement membrane and the occurrence of small pores in the podocytes of the.
Pseudo-Bartter syndrome is a general term that refers to certain conditions that cause similar symptoms and signs of Bartter syndrome but in which there is no inherited renal tubular dysfunction. Gitelman syndrome is usually diagnosed in teens or adults. This causes a rise in the level of the aldosterone and makes the kidneys remove too much potassium from the body.
Clinical manifestations and treatment of hypokalemia in adults. People with Bartter syndrome lose too much sodium through the urine. Signs and symptoms of Bartter syndrome include.
It is also due to salt losses and reasons for these include the use of certain diuretics conditions in which frequent vomiting occurs including. Etiology and diagnosis of distal type 1 and proximal type 2 renal tubular acidosis. To assist in the secondary care diagnosis and treatment of chronic cough as the solely presenting symptom if chest radiography and lung function tests remain inconclusive.
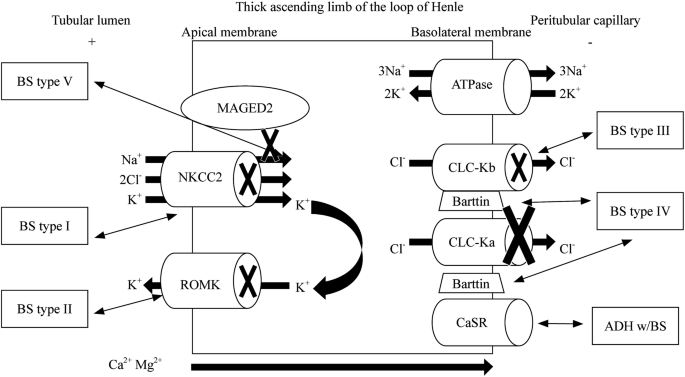
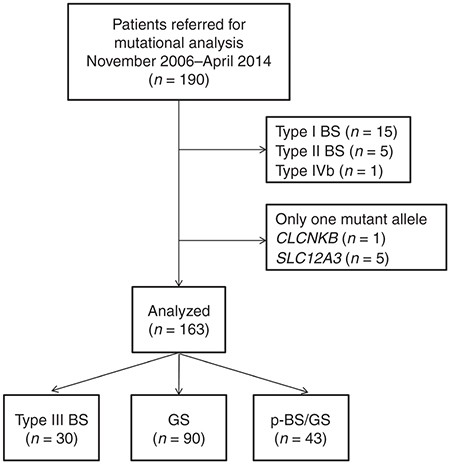
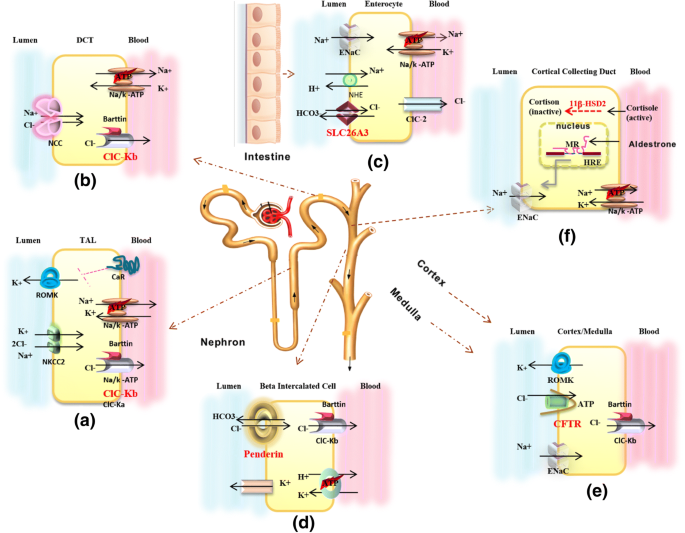
Clinical manifestations diagnosis and management. Gitelman syndrome GS is an autosomal recessive kidney tubule disorder characterized by low blood levels of potassium and magnesium decreased excretion of calcium in the urine and elevated blood pH. Bartter and Gitelman syndromes.
To illustrate reasonable and cost-effective management of cough one of the most frequent reasons for primary care consultations. Diagnosis of primary aldosteronism.
Bartter and Gitelman syndromes.
People with Bartter syndrome lose too much sodium through the urine. Bartter syndrome is usually diagnosed in early childhood. People with Bartter syndrome lose too much sodium through the urine. The disorder is caused by genetic mutations resulting in improper function of the thiazide-sensitive sodium-chloride symporter SLC12A3 also known as NCC NCCT or. Diagnosis of primary aldosteronism. To assist in the secondary care diagnosis and treatment of chronic cough as the solely presenting symptom if chest radiography and lung function tests remain inconclusive. Bartter syndrome and Gitelman syndrome can both cause metabolic alkalosis. To illustrate reasonable and cost-effective management of cough one of the most frequent reasons for primary care consultations. It is also due to salt losses and reasons for these include the use of certain diuretics conditions in which frequent vomiting occurs including.
Signs and symptoms of Bartter syndrome include. They also affect your kidneys. This causes a rise in the level of the aldosterone and makes the kidneys remove too much potassium from the body. Gitelman syndrome GS is an autosomal recessive kidney tubule disorder characterized by low blood levels of potassium and magnesium decreased excretion of calcium in the urine and elevated blood pH. The disorder is caused by genetic mutations resulting in improper function of the thiazide-sensitive sodium-chloride symporter SLC12A3 also known as NCC NCCT or. Bartter syndrome and Gitelman syndrome can both cause metabolic alkalosis. Nephritic syndrome is a syndrome comprising signs of nephritis which is kidney disease involving inflammationIt often occurs in the glomerulus where it is called glomerulonephritisGlomerulonephritis is characterized by inflammation and thinning of the glomerular basement membrane and the occurrence of small pores in the podocytes of the.

































Post a Comment for "Bartter Syndrome In Adults"