Cauda Equina Vs Conus Medullaris Syndrome
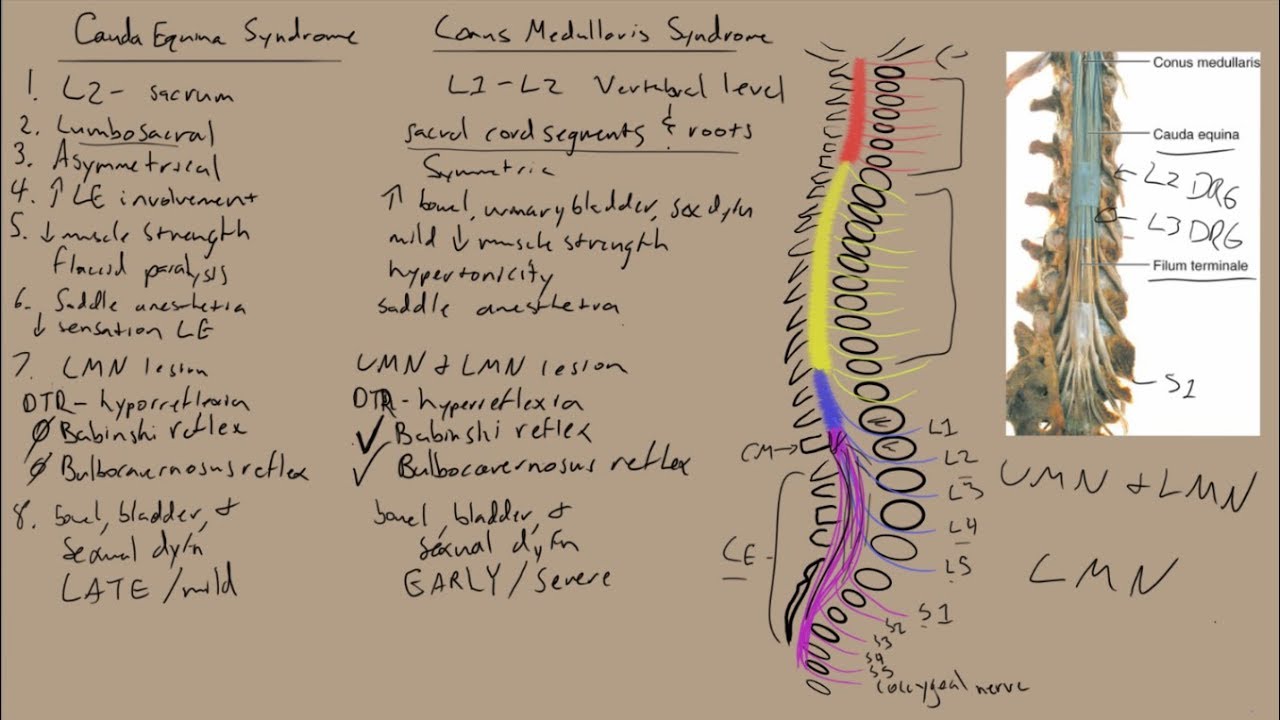
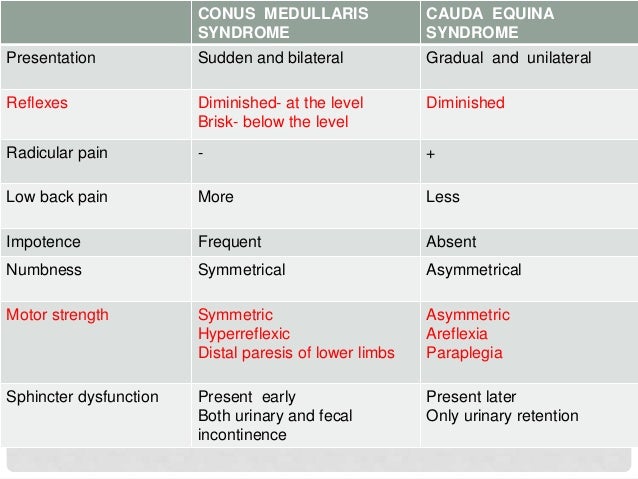
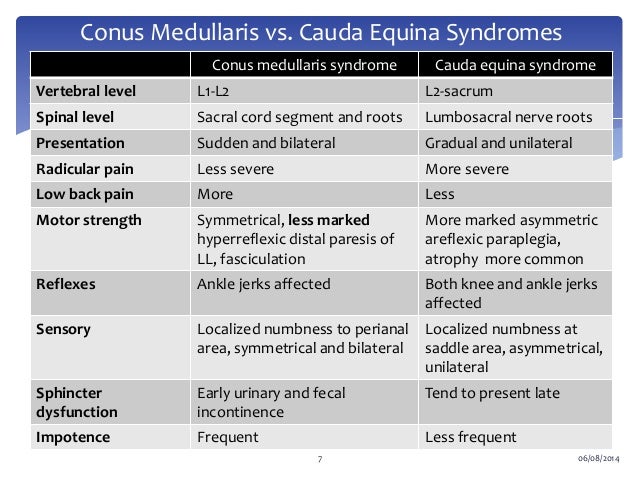
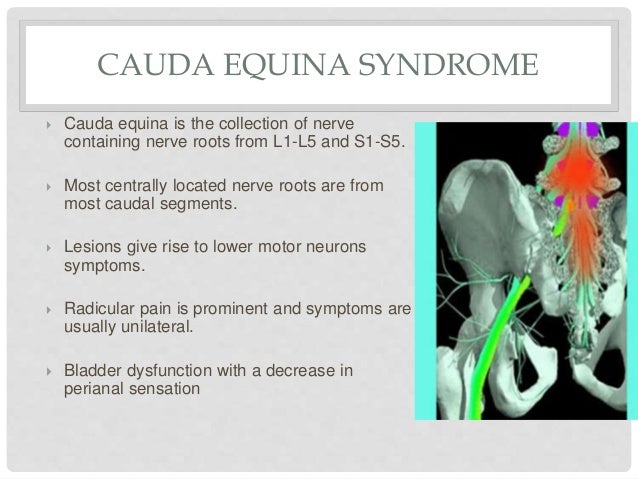
Cauda equina vs conus medullaris syndrome. Cauda equina syndrome refers to a collection of symptoms and signs that result from severe compression of the descending lumbar and sacral nerve roots. Determine if patient is in spinal shock check bulbocavernosus reflex. Cauda equina syndrome considered a peripheral nerve.
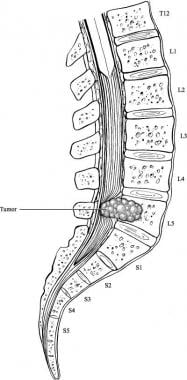
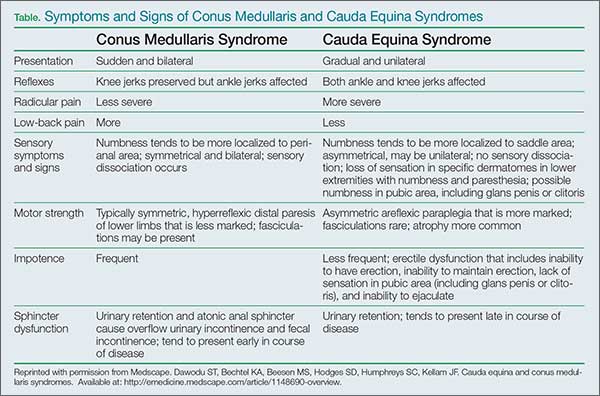
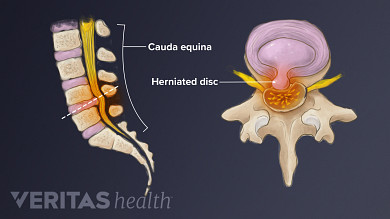
Cauda equina syndrome. In people with cauda equina syndrome compression is confined to the lumbar spine low back below the conus medullaris the lower part of the spinal cord. Last resort treatment of moderate to severe 5 or more on a 10-point VAS scale chronic neuropathic pain of certain origins ie lumbosacral arachnoiditis phantom limbstump pain peripheral neuropathy post-herpetic neuralgia intercostal neuralgia cauda equina injury incomplete spinal cord injury or plexopathy that is refractory to 12.
You do not need to experience all the signs of cauda equina syndrome for a diagnosis to be made or for you to seek out immediate medical attention. The investigators concluded that the combined SSEP and EMG monitoring of lower-limb muscles EAS and EUS is a practical and reliable method for obtaining optimal electrophysiological feedback during complex neurosurgical procedures involving the conus medullaris and cauda equina. Cauda equina syndrome is considered an incomplete cord syndrome even though it occurs below the conus.
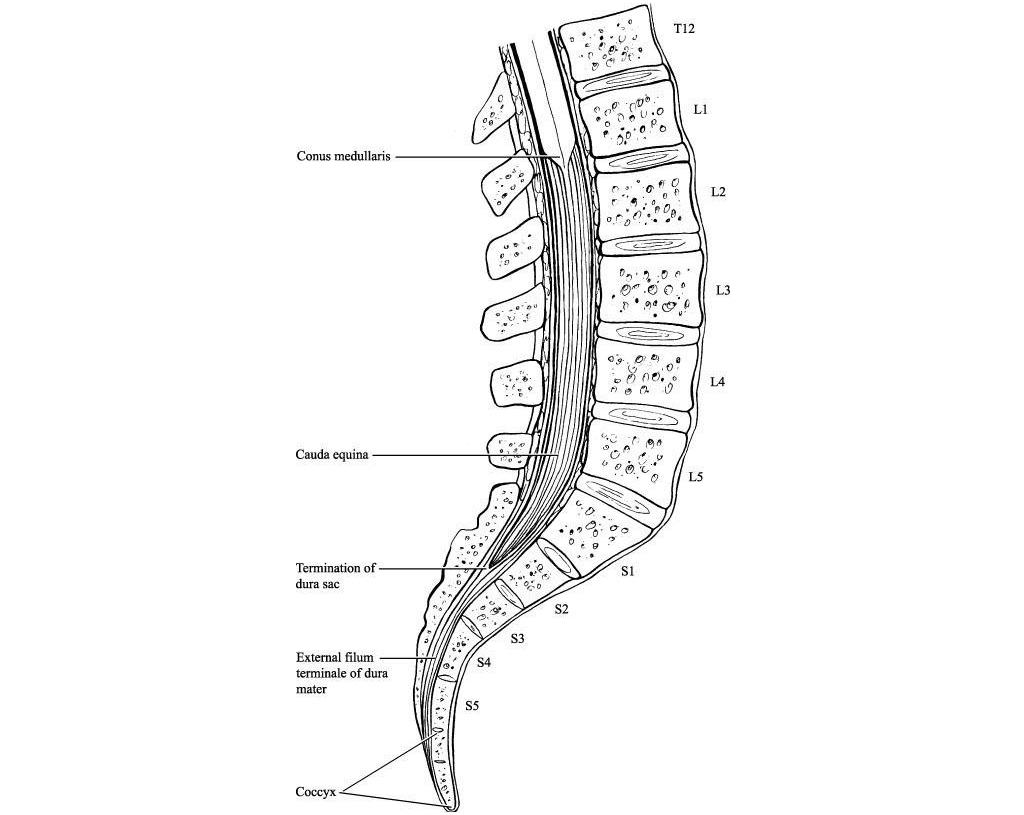
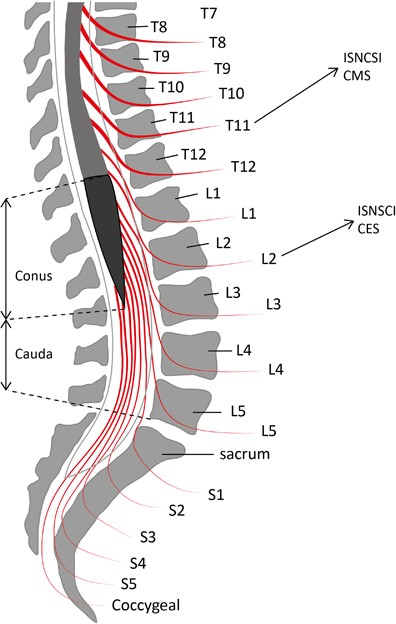
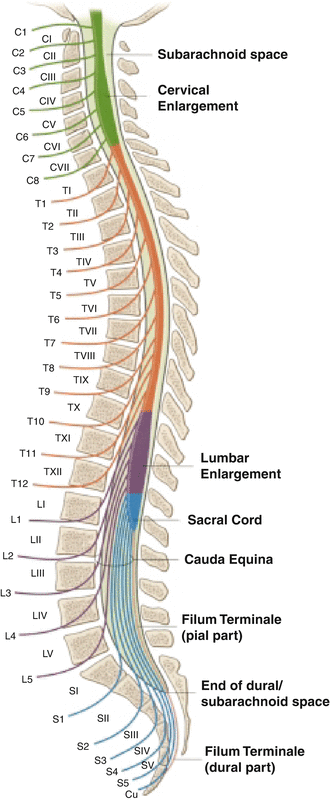
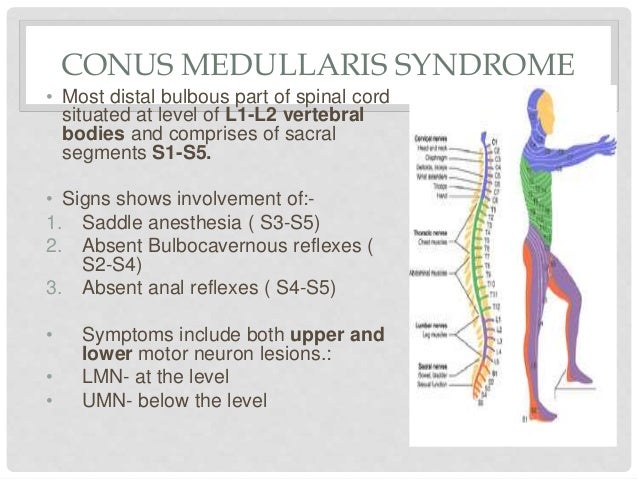
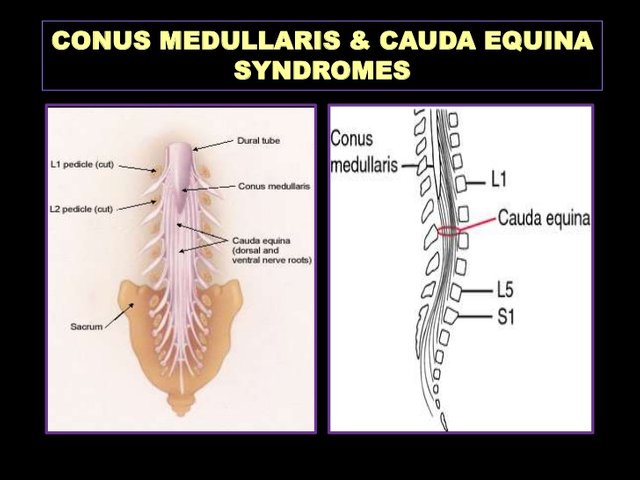
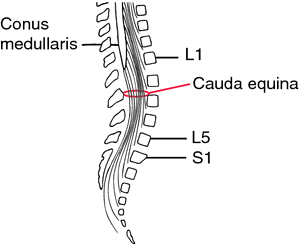
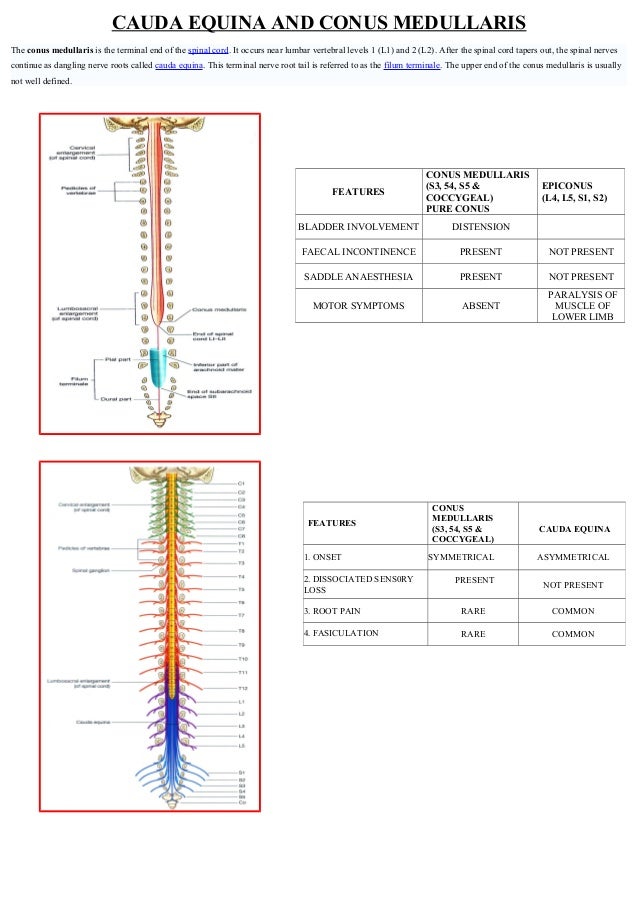
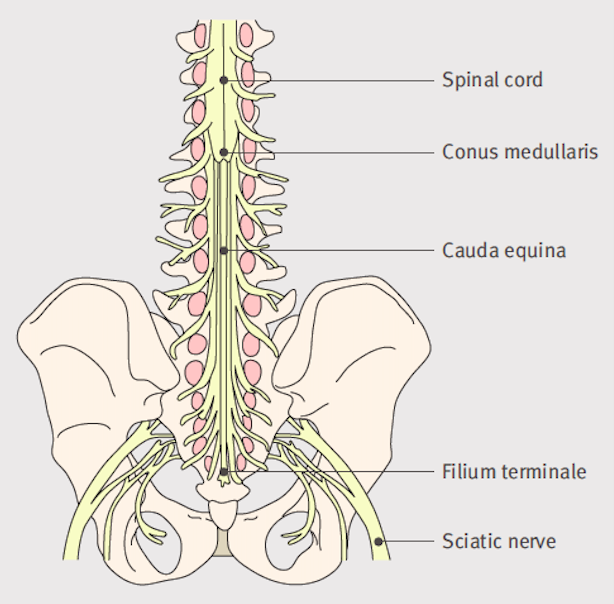
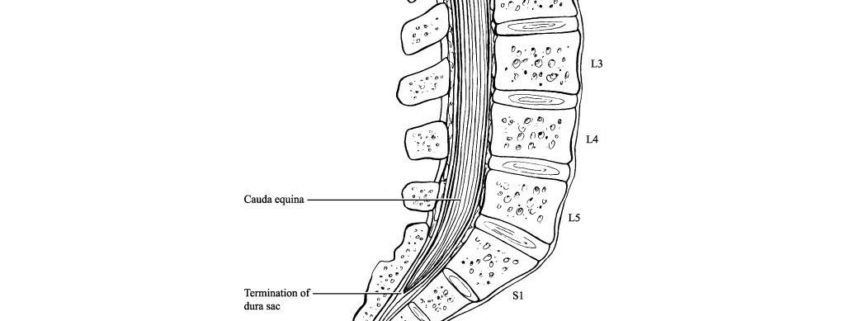
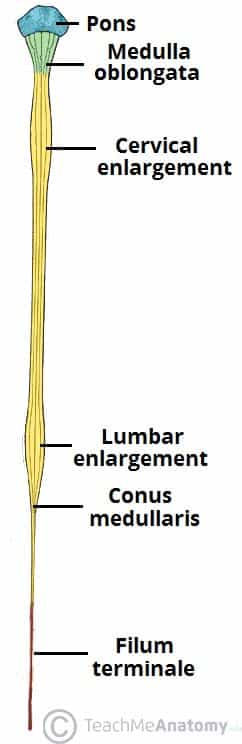
5 Diaphragmatic paralysis Neonatal Distal Ulnar-Median Recessive. Academiaedu is a platform for academics to share research papers. Posterior view of the lumbar region of the spinal canal demonstrating the conus medullaris at the L1 to L2 level and the cauda equina nerve roots inferiorly.
Lowest segment with intact sensation and antigravity 3 or more muscle function strength. Determine neurologic level of injury. Cauda Equina Conus medullaris Hemicord Posterior cord Spinal Muscular Atrophies Benign congenital with contractures Bulbo-Spinal Muscular Atrophy X-linked Kennedys Autosomal Dominant Distal SMA HMN 1.
Cauda equina syndrome considered a peripheral nerve.
Determine if patient is in spinal shock check bulbocavernosus reflex. Cauda equina syndrome. Academiaedu is a platform for academics to share research papers. 5 Diaphragmatic paralysis Neonatal Distal Ulnar-Median Recessive. You do not need to experience all the signs of cauda equina syndrome for a diagnosis to be made or for you to seek out immediate medical attention. Cauda equina syndrome refers to a collection of symptoms and signs that result from severe compression of the descending lumbar and sacral nerve roots. Lowest segment with intact sensation and antigravity 3 or more muscle function strength. Determine neurologic level of injury. Last resort treatment of moderate to severe 5 or more on a 10-point VAS scale chronic neuropathic pain of certain origins ie lumbosacral arachnoiditis phantom limbstump pain peripheral neuropathy post-herpetic neuralgia intercostal neuralgia cauda equina injury incomplete spinal cord injury or plexopathy that is refractory to 12.
The investigators concluded that the combined SSEP and EMG monitoring of lower-limb muscles EAS and EUS is a practical and reliable method for obtaining optimal electrophysiological feedback during complex neurosurgical procedures involving the conus medullaris and cauda equina. Cauda equina syndrome refers to a collection of symptoms and signs that result from severe compression of the descending lumbar and sacral nerve roots. 5 Diaphragmatic paralysis Neonatal Distal Ulnar-Median Recessive. Academiaedu is a platform for academics to share research papers. The investigators concluded that the combined SSEP and EMG monitoring of lower-limb muscles EAS and EUS is a practical and reliable method for obtaining optimal electrophysiological feedback during complex neurosurgical procedures involving the conus medullaris and cauda equina. Cauda equina syndrome considered a peripheral nerve. Determine if patient is in spinal shock check bulbocavernosus reflex.





























Post a Comment for "Cauda Equina Vs Conus Medullaris Syndrome"