Digeorge Syndrome Immune System
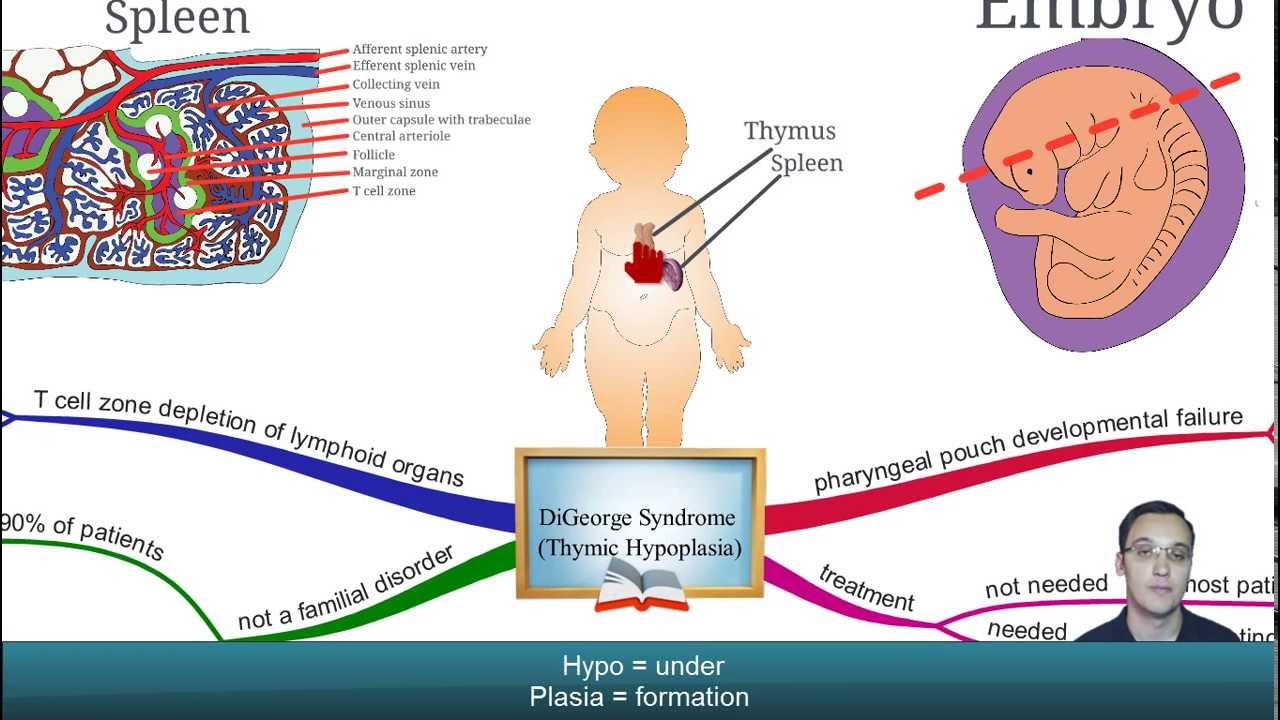
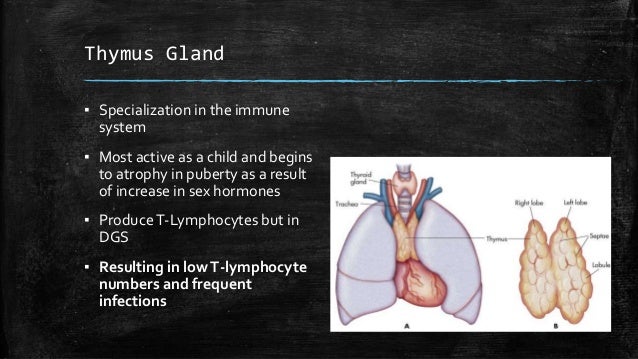
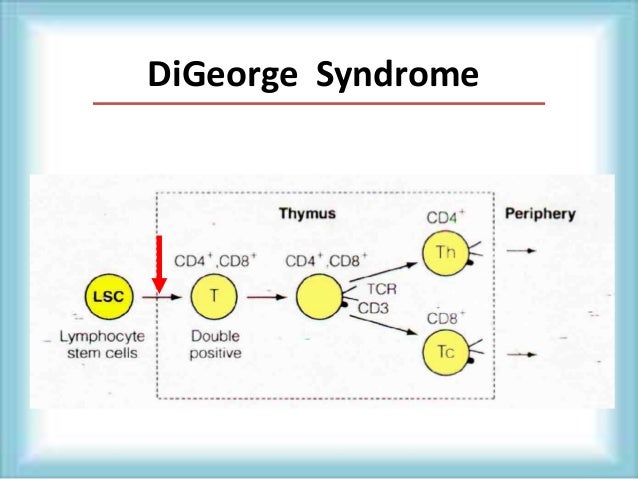
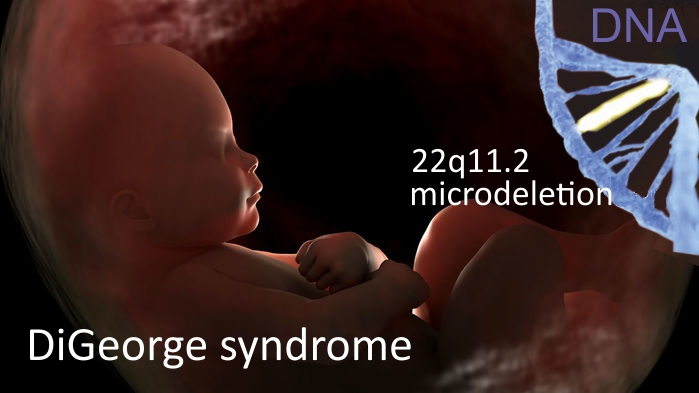
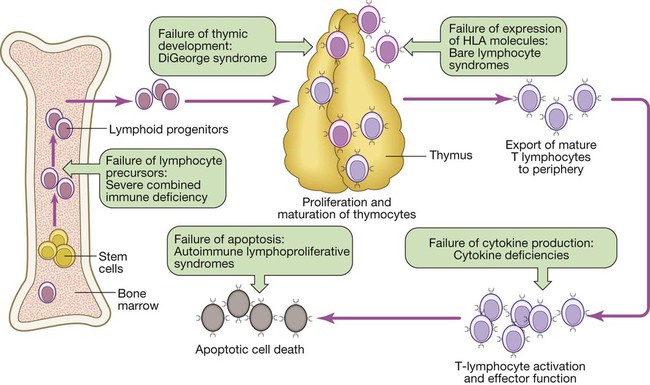
Digeorge syndrome immune system. DiGeorge syndrome is a chromosomal disorder that typically affects the 22nd chromosome. Angelo DiGeorge had immunodeficiency as a central component. DiGeorge syndrome is the most common of these with recognizable physical characteristics and is caused from the lack of a thymus gland largely responsible for T lymphocyte production.
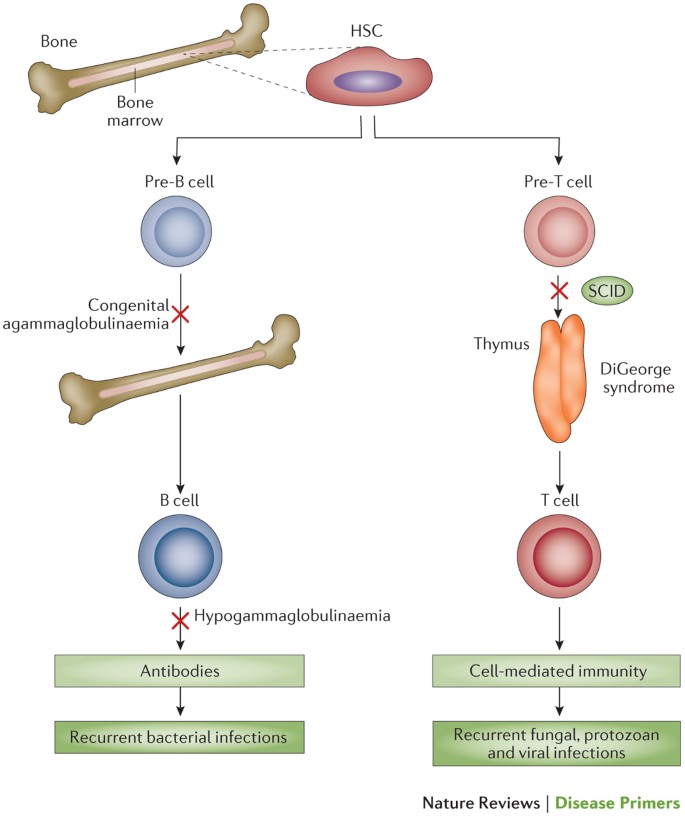
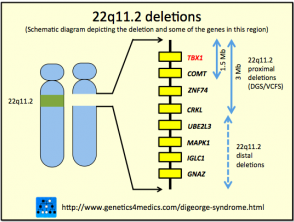
Most people with DiGeorge syndrome are missing a small piece of chromosome 22 known as 22q112. Disturbance of cervical neural crest migration into the derivatives of the pharyngeal arches and pouches can account for the phenotype. Combined immune deficiencies result from a lack of both B and T lymphocytes.
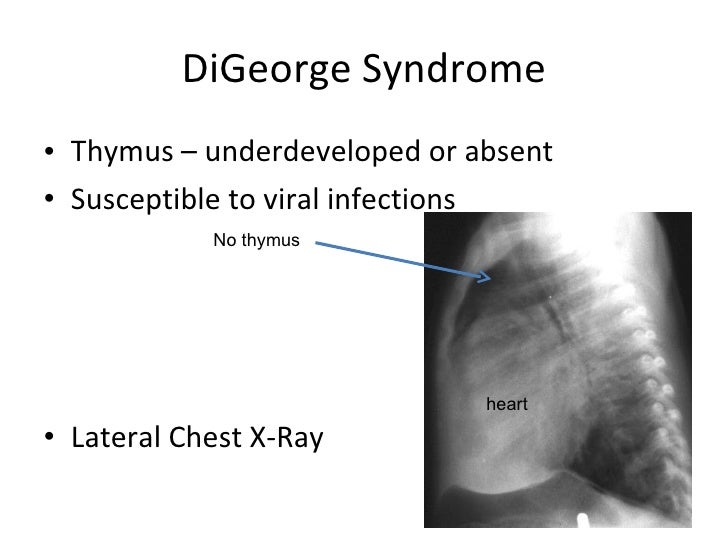
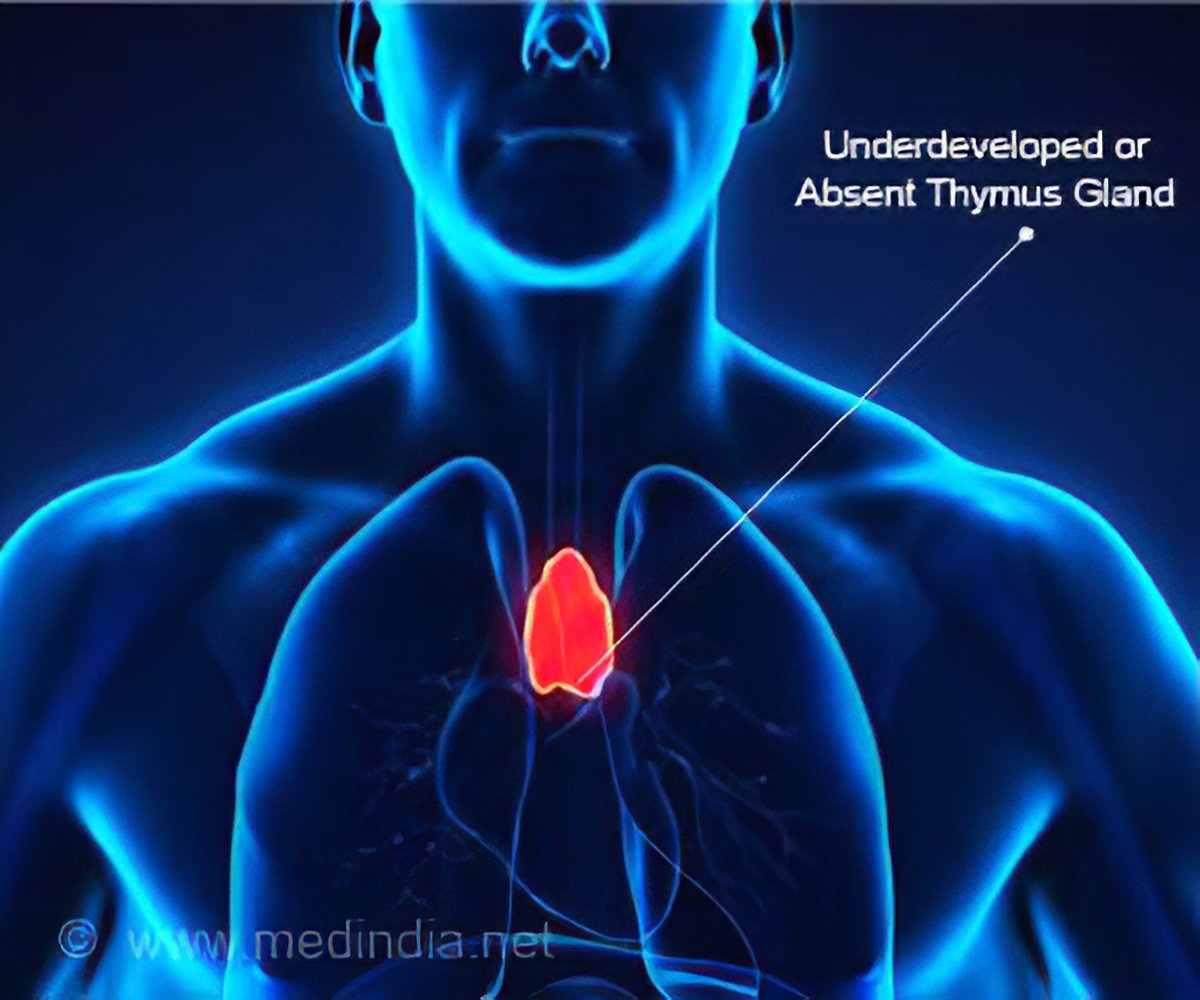
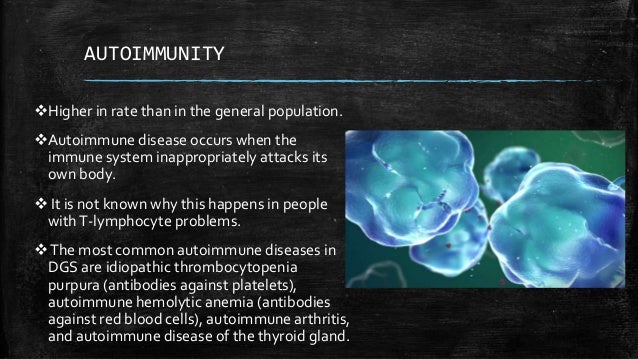
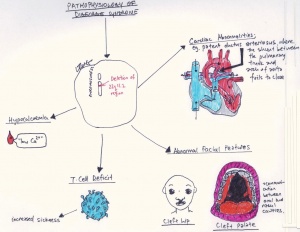
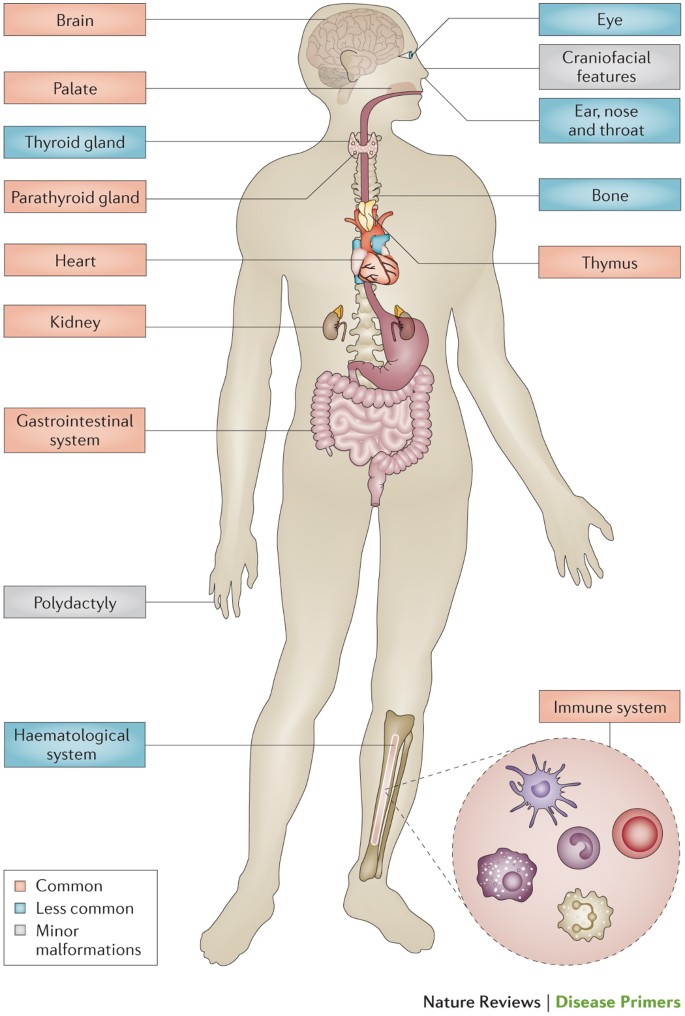
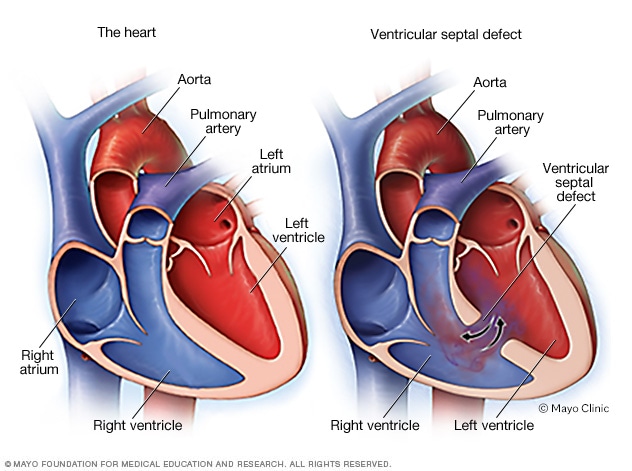
Autoimmunity is when the bodys immune system accidentally harms healthy tissue. These problems usually present at a babys birth or in early childhood include heart defects an impaired immune system and developmental delays. Children with DiGeorge syndrome are born with several abnormalities including heart defects underdeveloped or absent parathyroid glands an underdeveloped or absent thymus gland and characteristic facial features.
In immune system disorder. Autoimmunity is treatable and is less frequent after the first year after transplantation. The clinical features can vary but can be remembered with the CATCH-22 acroynm.
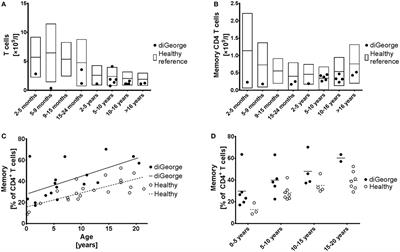
DGS patients with low naive CD4 T and CD8 T cells were defined as high-risk HR patients whereas patients with normal numbers of naive CD4 and CD8 T cells were defined as standard risk SR patients. Angelo DiGeorge in 1965 as a clinical trial that included immunodeficiency hypoparathyroidism and. Consequently the infant has either no mature T cells or very few.
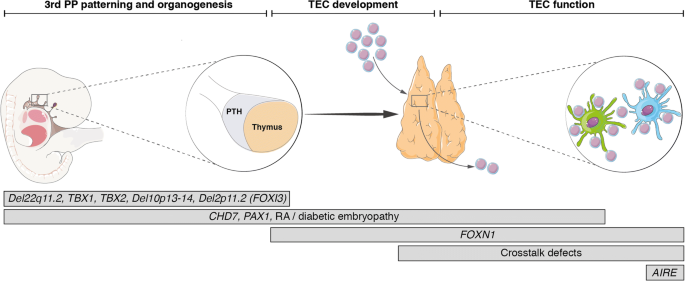
The syndrome originally described by Dr. DiGeorge Syndrome DGS is a combination of signs and symptoms caused by defects in the development of structures derived from the pharyngeal arches during embryogenesis. Features of DGS were first described in 1828 but properly reported by Dr.
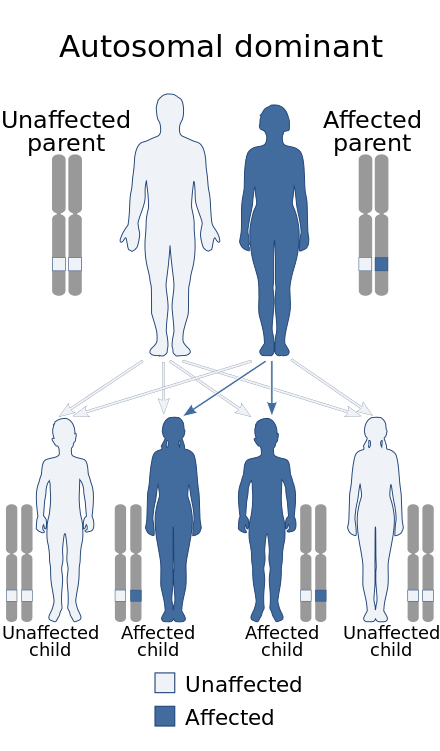
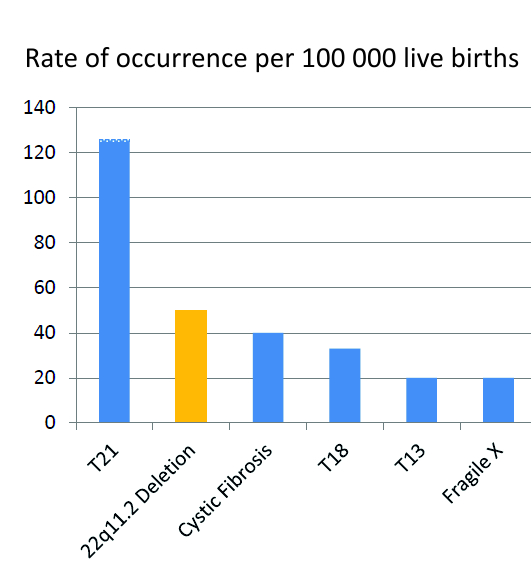
DiGeorge or 22q112 deletion syndrome is autosomal dominant and caused by a deletion of the q112 portion of chromosome 22. DiGeorge syndrome is a genetic disorder that can affect many parts of the body.
Autoimmunity is when the bodys immune system accidentally harms healthy tissue.
DiGeorge syndrome DGS comprises hypocalcemia arising from parathyroid hypoplasia thymic hypoplasia and outflow tract defects of the heart. DiGeorge syndrome is a genetic disorder that can affect many parts of the body. Features of DGS were first described in 1828 but properly reported by Dr. DiGeorge syndrome is a chromosomal disorder that typically affects the 22nd chromosome. DiGeorge or 22q112 deletion syndrome is autosomal dominant and caused by a deletion of the q112 portion of chromosome 22. DGS is caused by irregular cell and tissue growth during fetal development. The clinical features can vary but can be remembered with the CATCH-22 acroynm. Several body systems develop poorly and there may. DiGeorge syndrome is the most common of these with recognizable physical characteristics and is caused from the lack of a thymus gland largely responsible for T lymphocyte production.
The thymus is the school house where T-cells are. DiGeorge syndrome is a genetic disorder that can affect many parts of the body. DiGeorge syndrome also called 22q11 deletion syndrome congenital thymic hypoplasia or third and fourth pharyngeal pouch syndrome is a birth defect that is caused by an abnormality in chromosome 22 and affects the babys immune system. DiGeorge Syndrome DGS is a combination of signs and symptoms caused by defects in the development of structures derived from the pharyngeal arches during embryogenesis. Children with DiGeorge syndrome are born with several abnormalities including heart defects underdeveloped or absent parathyroid glands an underdeveloped or absent thymus gland and characteristic facial features. T cells are white blood cells that are important for protection against infections. In immune system disorder.

























Post a Comment for "Digeorge Syndrome Immune System"